Shopping cart
No Widget Added
Please add some widget in Offcanvs Sidebar
- 210 68 24 604
- Email: info@psennis.com
Please add some widget in Offcanvs Sidebar

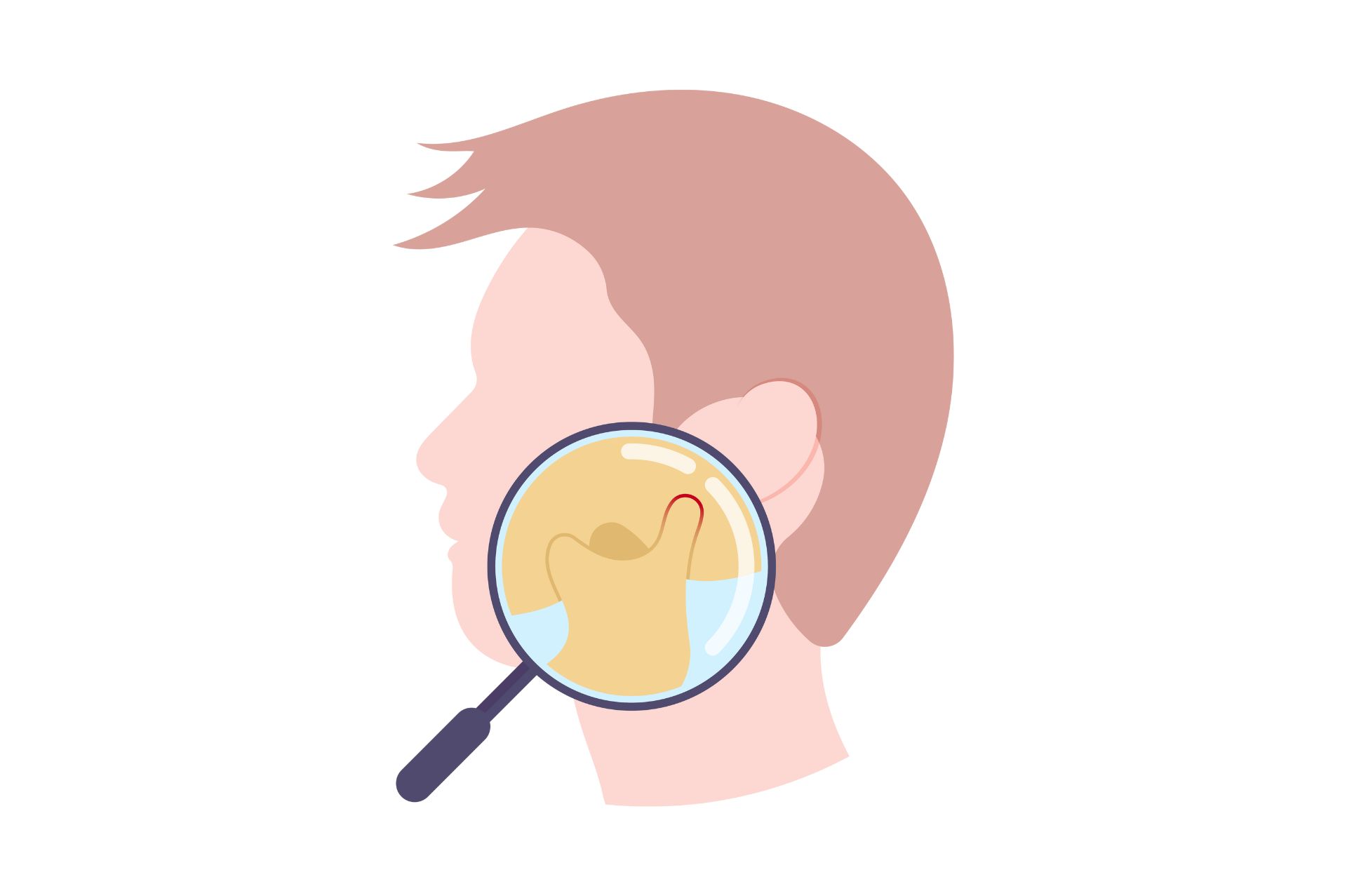
A wisdom tooth, also known as a third molar, is most likely to cause problems when it remains impacted or semi-impacted within the jaw.
The wisdom tooth is the last tooth to appear in the mouth, but it often brings with it problems and questions about the health of our teeth.
The average adult has 32 teeth at the age of 18, 16 in the upper jaw and 16 in the lower. Each of the teeth in the mouth has a specific name, location, and function.
The teeth located at the front of the mouth (incisors, canines, premolars) have the task of grasping and cutting food into smaller pieces.
The back teeth (molars) serve to grind food, making it suitable for swallowing.
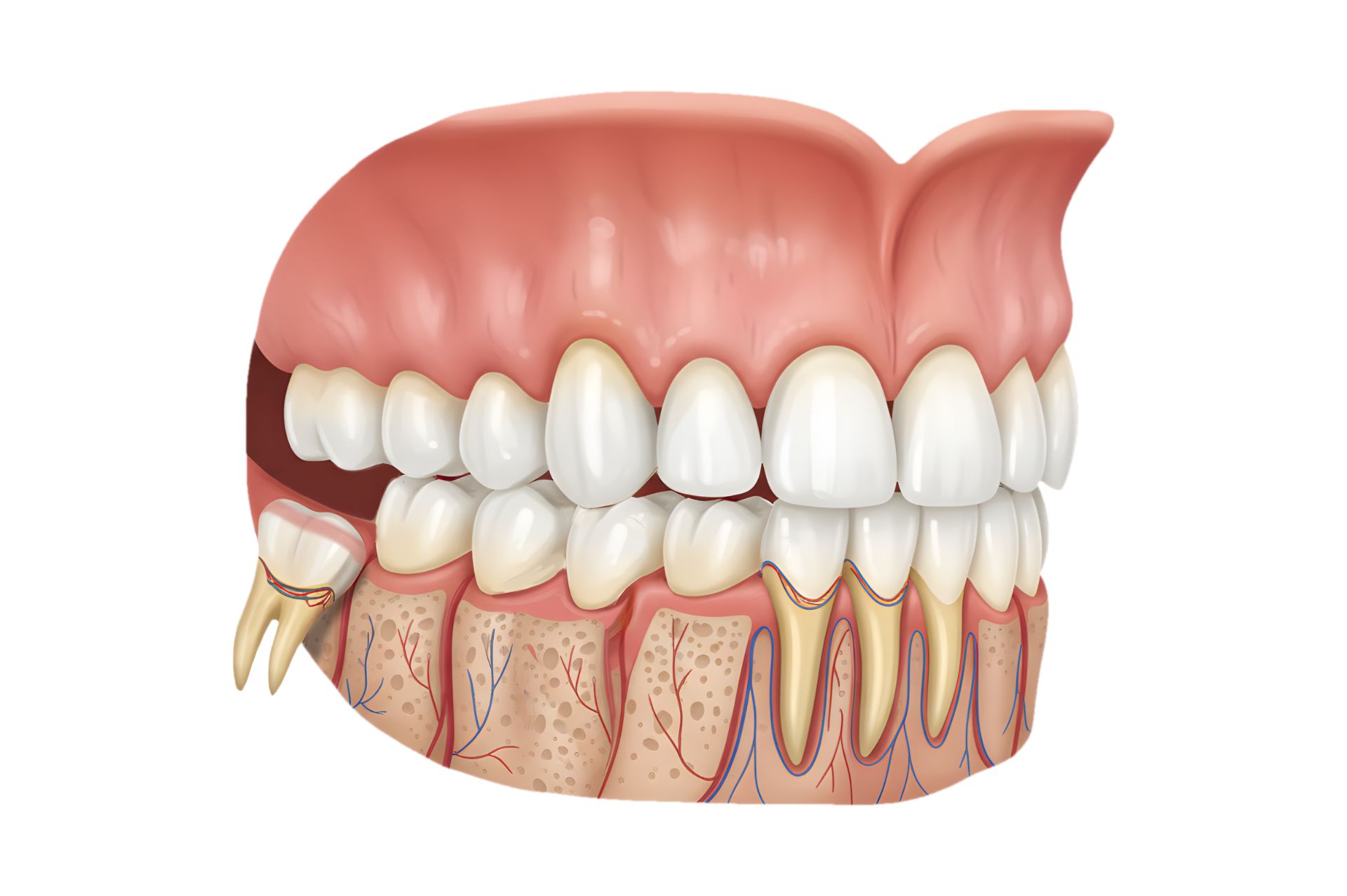
However, the average mouth only has room for 28 teeth to fully erupt and settle into the jaws. It can be very difficult and painful to settle 32 teeth into the space provided for 28.
The 4 teeth that are required to fit into the above space are the 3rd molars, or wisdom teeth.
Τα 4 δόντια που καλούνται να χωρέσουν στον παραπάνω χώρο είναι οι 3οι γομφίοι, ή φρονιμίτες.
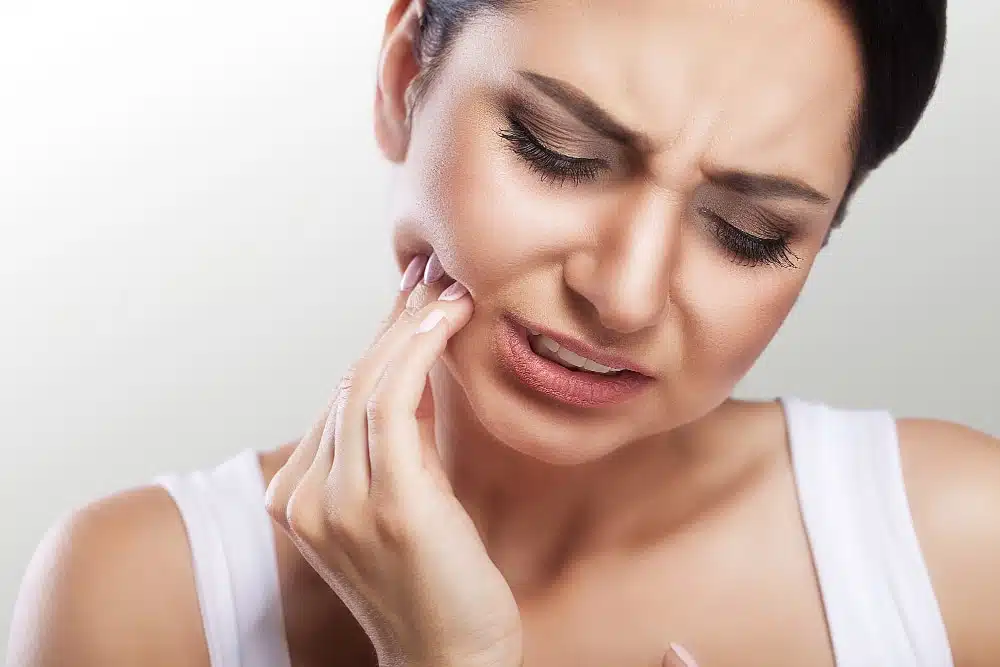
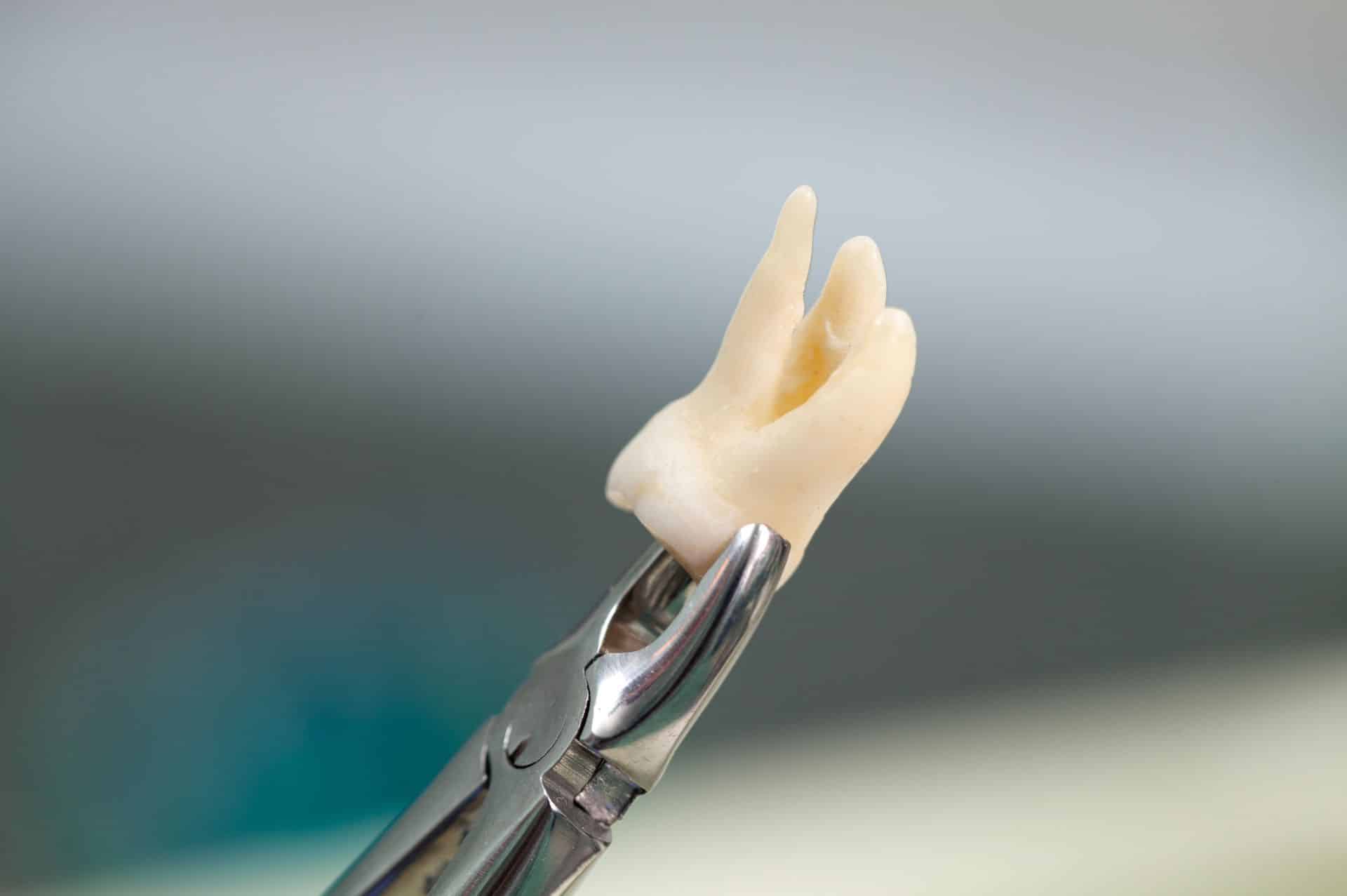
A wisdom tooth, also known as a third molar, is very likely to cause problems when it remains impacted or semi-impacted in the jaw. Surgical extraction of an impacted wisdom tooth is often performed to protect the second molars from damage or displacement from the pressure exerted. After extraction, care and proper healing are required to avoid complications.
The removal of a wisdom tooth can be performed under local anesthesia, intravenous sedation (anesthesia) or, in special cases, under general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the extraction and the patient’s needs.
These procedures are performed with absolute safety by Maxillofacial Surgeon Panagiotis Sennis, in collaboration with experienced anesthesiologists, within a fully equipped medical environment that meets all safety protocols.
The type of anesthesia that will be used in wisdom tooth extraction, as well as the specifics of wisdom tooth extraction (such as proximity to the inferior alveolar nerve, relationship to the sinus antrum, etc.), will be evaluated and discussed in detail during the clinical examination, with answers to any questions the patient may have.

You will remain in the doctor’s office for approximately 15 minutes until we determine that you can go home without any problems.
When you are ready, you will be given post-operative instructions, prescribed medication, and a date for a re-check in 1 week.
Wisdom teeth, or third molars, are the last teeth to erupt in the mouth, usually between the ages of 17 and 25. When they erupt properly and are surrounded by healthy gums, their removal is not required.
Unfortunately, this does not happen often. In the majority of cases, their emergence is hindered by a lack of space in the jaws. This results in them remaining impacted (under the gums or bone) or semi-impacted (partially protruding into the mouth).
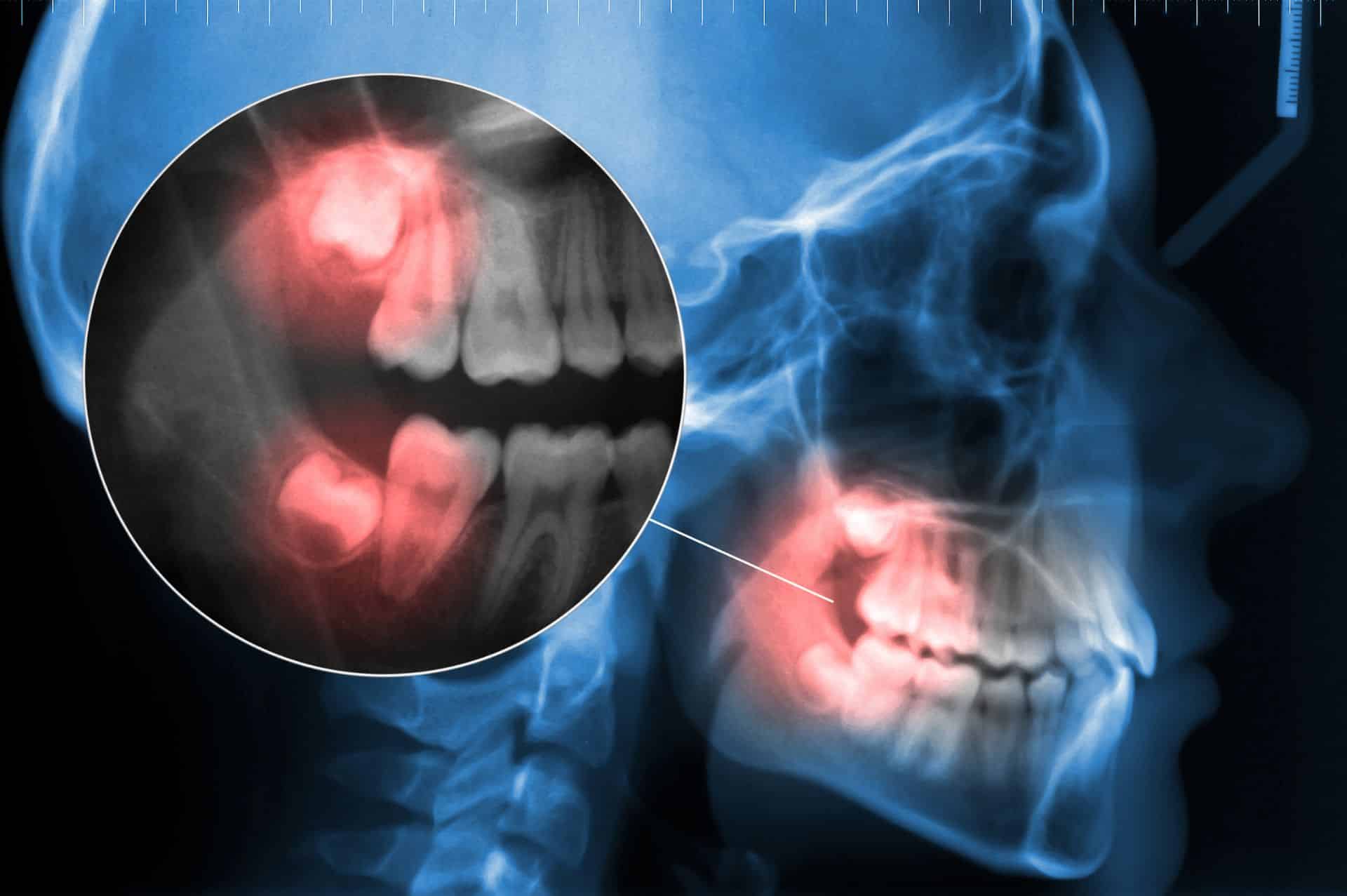
Wisdom teeth in the wrong position can create multiple oral health problems:

When the wisdom tooth is partially impacted , the small opening in the gums around it allows bacteria to enter . This leads to inflammation of the gums (periodontitis), with symptoms such as:
Wisdom teeth, trying to erupt into insufficient space , may push on adjacent teeth , causing:
(for people who wear braces)

According to recent studies , the incidence of cysts or benign tumors around impacted wisdom teeth ranges between 32% and 35% . Furthermore, the probability of someone developing a problem with a wisdom tooth during their lifetime reaches 65% .
The most serious problem is related to the formation of cysts or even benign tumors around impacted wisdom teeth. These lesions can lead to:
With age, wisdom teeth become more difficult to clean , increasing the risk of:
Cervical cancer, both in the wisdom tooth and the adjacent tooth
Periodontal diseases, i.e. inflammation and loss of gum support

Preventive extraction of impacted or semi-impacted wisdom teeth at a young age (usually before age 25) offers:
Proper clinical and radiographic evaluation is crucial for the extraction decision. The maxillofacial surgeon or dentist examines:
The position of the wisdom tooth within the jaw
The relationship with important anatomical structures , such as the inferior alveolar nerve or the sinus antrum
The presence of inflammation, cyst, or pain
Panoramic X-ray or computed tomography (CBCT) provide a complete picture for planning the operation.
Early diagnosis in adolescence helps:
Typically, patients are referred by their general dentist, orthodontist, or are referred directly to an oral surgeon for specialized evaluation.
