Shopping cart
No Widget Added
Please add some widget in Offcanvs Sidebar
- 210 68 24 604
- Email: info@psennis.com
Please add some widget in Offcanvs Sidebar
For the successful placement of dental implants, it is often necessary to strengthen the area using bone graft, which is taken from the patient themselves or from specially processed materials.
Bone grafts are used to restore bone loss and prepare the jaw for the placement of dental implants.
Over time, the jawbone in areas where teeth have been lost atrophies or is absorbed.
This results in less bone than necessary to accommodate dental implants in the area. In these cases, patients are unable to obtain/place dental implants.
After the extraction of one or more teeth, bone loss is a common occurrence, especially due to the normal resorption of the alveolar ridge.
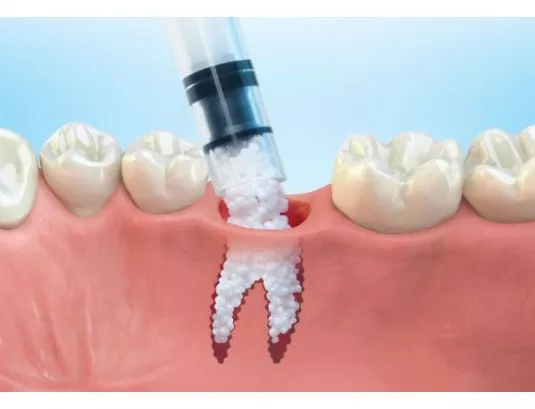
For the successful placement of dental implants, it is often necessary to strengthen the area using bone graft, which is taken from the patient themselves or from specially processed materials.
In some cases, sinus floor elevation may be necessary, especially during preparation for implant placement in the upper jaw. This intervention is performed under strict surgical conditions to ensure success after treatment.
Bone grafting can correct areas where we are considering placing dental implants and which lack the necessary bone. This may be due to a previous extraction, periodontitis or even after an injury. The bone that will be used for reconstruction can be taken from a “bone graft bank” or from the patient himself.
In the latter case and depending on the amount needed, it will be taken from the lower jaw, either the tibia or finally from the iliac bone (pelvis). Bone grafts are also placed in the sinus antrum with a technique called “sinus lift” to increase the bone in the posterior area of the upper jaw.
In all cases of bone regeneration, in addition to the bone, an absorbable membrane is placed which protects the graft while it is integrated into the jaw and then absorbed. The technique of jaw bone regeneration is called directed bone regeneration and usually takes 6 months to complete.
Extensive bone reconstruction of the jaws is usually performed after accidents in the facial area accompanied by multiple fractures, surgical removal of jaw tumors or during surgical correction of congenital anomalies. In these cases, bone grafts from the patient’s own body are used, the procedures are extensive and are performed in a hospital under general anesthesia.
The “sinuses” or “sinuses antra” are two air-filled cavities in the back of the upper jaw, one on each side. Some of the roots of the back teeth of the upper jaw naturally enter into them.
When these teeth are lost, the bone that held them becomes increasingly thinner, resulting in it no longer being able to hold dental implants that will replace the lost teeth.
In these cases, the bone needs to be increased and this is done with a technique called “sinus bone regeneration” or “sinus bone regeneration with elevation”.
The entrance to the sinus is through the mouth from the point where the lost teeth are located.
Using bone from the patient’s own body usually gives the best results.
There are various areas of the body from which bone grafts can be taken. In the maxillofacial region, bone grafts can be taken from inside the mouth from the area of the chin, wisdom tooth, or in the case of the upper jaw behind the last tooth.
In more extensive deficits, where a larger amount of bone graft is needed, the areas chosen as donors are the iliac bone (pelvis) and the tibia of the leg.
In many cases, we can use allogeneic grafts along with dental implants in areas where we need a small amount of bone.
Allogeneic bone comes from donor organ banks and is specially processed so that it can be used to fill bone defects.
When allogeneic bone grafts are placed in the defect area, they promote osteogenesis so that the patient’s own bone can grow into the defect area. Allogeneic grafts are very safe and very effective.
Synthetic bone grafts are also used either alone or in combination with the patient’s own bone.
Synthetic implants are largely absorbed by the body, biodegradable, and usually eliminated in 6-8 months.
During this time, they hold the space in which they were placed, preventing the gums from eroding it, and at the same time, they activate the body to produce its own bone.
It is gradually replaced by the patient’s bone so that over the above period, they are almost not detected in the area where they were placed and have been completely replaced by the patient’s bone.
Depending on their severity, these procedures are performed either under general anesthesia or under “sedation”, in a hospital environment.
Το κόστος ενός εμφυτεύματος δοντιού ποικίλλει ανάλογα με:
Στην Ελλάδα, η τιμή ανά μονάδα εμφυτεύματος κυμαίνεται συνήθως από 700€ έως 1.500€, συμπεριλαμβανομένης της τελικής στεφάνης.
Τα εμφυτεύματα δοντιών μπορούν να διαρκέσουν 15–25 χρόνια ή και περισσότερο, εφόσον ο ασθενής: